1. General provisions on renewal of validity of protection titles
Industrial design patents shall have a validity starting from the grant date and expiring at the end of 5 years after the filing date and may be renewed for two consecutive terms, each of 5 years. Request for renewal of one or several industrial design variations stated in the industrial design patent must include a basic variation.
To have the validity of his/ her industrial design protection title renewed, a protection title holder shall file a request for renewal of protection titles’ validity and pay a validity renewal fee within six months before the expiration of the validity term. The payment of the validity renewal fee may be delayed for no more than six months after the expiration of the current validity term but the protection title holder shall pay the delayed renewal fee for each month of delayed payment.
– A request for renewal of protection titles’ validity includes:
+ Declaration requesting renewal of protection titles’ validity (according to form 02-GH/DTVB AppendixC of Circular No. 01/2007/ TT-BKHCN);
+ Original protection title (if the extension is requested to be recorded in the protection title);
+ Power of attorney (in case the request is filed through a representative);
+ A copy of the receipt of fees and charges as prescribed;
+ Other documents (if necessary).
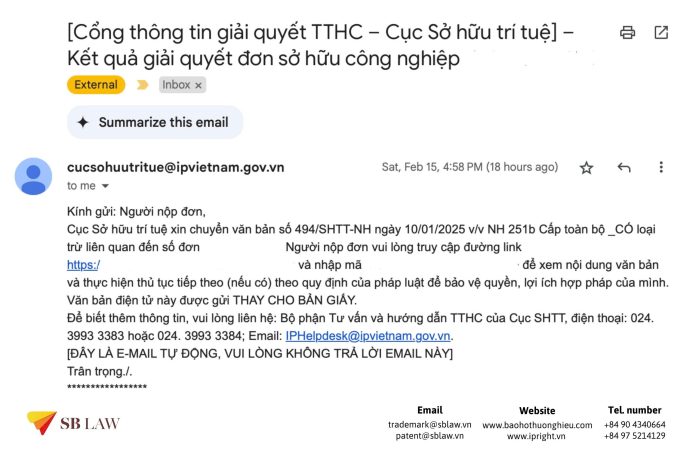
– The time limit: IPVN shall examine the request for validity renewal within 01 month from the date of receipt of the request.
– Result: If the request is considered valid, the IPVN shall issue a decision on renewal of the protection title, register and publish it in the Industrial Property Official Gazette. If the request is considered invalid, the IPVN shall send to the requester a notice on its intended refusal. If within a set time limit the requester fails to correct errors or unsatisfactorily corrects errors, makes no opposition or an unreasonable opposition, the IPVN shall issue a decision on its rejection of the request for protection title renewal.
Return the protection title to the owner.
– Fees and charges:
+ Official charge for renewal of protection titles: VND 100,000/ 01 variant;
+ Official charge for delayed renewal: renewal fee plus 10% for each month of delayed payment;
+ Fee for examination request for renewal of protection titles: VND 160,000/ 01 protection title;
+ Fee for protection title usage: VND 700,000/ 01 variant;
+ Fee for publication of decision of renewal of protection titles: VND 120,000/ 01 request;
+ Fee for recording decision of renewal or change of holders of protection titles into the National Register of Industrial Property: VND 120,000/ protection title.
2. General provisions on grant of protection title duplicates and reissue of protection titles
In case the industrial property rights are under co-ownership, a protection title shall only be granted to the first person named in the list of co-applicants. Other co-holders may request the IPVN to grant duplicates of the protection title but shall pay a fee therefor.
In the following cases, an industrial property right holder who has been granted a protection title/duplicate of protection title may request the IPVN to reissue the protection title/duplicate of protection title but shall pay a reissue fee: the protection title/duplicate of protection title is lost; damaged, torn, stained or faded out that it can no longer be used.
– A request for grant of duplicates/ reissue of protection titles includes:
+ Declaration requesting grant of duplicates/ reissue of protection titles, (typing according to form 03-PBVB/GCN Appendix C of Circular No. 01/2007/ TT-BKHCN);
+ Sets of photos or drawings of industrial designs;
+ Power of attorney (in case the request is filed through a representative);
+ A copy of the receipt of fees and charges as prescribed;
+ Other documents (if necessary).
– The time limit: IPVN shall examine the request for grant of duplicates/reissue of protection titles within 01 month from the date of receipt of the request.
– Result: If that request satisfies the above requirements, the IPVN shall issue a decision on the grant of a protection title duplicate/reissue of the protection title and record it in the section for registration of the protection title in the National Register of Industrial Property, and publish it in the Industrial Property Gazette. If a request for duplicate/ reissue of a protection title fails to satisfy the requirements above, the IPVN shall issue a decision on its refusal to grant duplicates/ refusal to reissue the protection title.
Return the protection title to the owner.
– Fees and charges:
+ Fee for publication of a decision on the grant of a protection title duplicate/ reissue of the protection title: VND 120,000/ 01 request;
+ Fee for recording a decision on the grant of a protection title duplicate/ reissue of the protection title into the National Register of Industrial Property: VND 120,000/ protection title.
+ Public service fee (temporarily not calculated, will be collected when there are specific regulations).
3. General provisions on amendment or change of holders of protection titles
The holder of a protection title may request the IPVN to record changes in that protection title in the following cases: Change in the name or address of the protection title holder; change in the author’s name or nationality; change of the protection title holder (transfer of ownership on the ground of inheritance, succession, merger, separation, split-up, joint venture, association or establishment of a new legal entity under the same owner, transformation of the business operation, or under a decision of a competent state agency…).
Record of changes related to information on industrial property representation service organizations on National Register of Industrial Property
A request for narrowing of the protection coverage: request for reduction of one or several independent or dependent points within the (requested) protection coverage stated in the industrial design patent.
– A written request for amendment or change of holders of protection titles comprises the following documents:
+ Written declaration requesting amendment of the protection title made according to a set form 01-SĐVB Appendix C of Circular No. 01/2007/ TT-BKHCN;
+ Original protection title;
+ Documents certifying the change of the name or address (the originals or notarized copies of the decision on rename or change of address; the business registration certificate that records the name or address change; other documents of legal validity evidencing the name or address change) in case the content requested to be modified is such name or address;
+ Documents evidencing the inheritance, succession, merger, separation, joint venture, association, establishment of a new legal entity under the same owner, transformation of business operation, or under a decision of a competent state agency;
+ Documents explaining in detail the modified contents;
+ 05 sets of photos or drawings of industrial designs;
+ Power of attorney (if the request is filed through a representative);
+ A copy of the receipt of fees and charges as prescribed;
+ Other documents (if necessary).
– The time limit: IPVN shall examine the requests for amendment of protection titles within 02 months from the date of receipt of the request.
In case of narrowing of the protection coverage, a re-examination must be conducted. Re-examination time limit: for industrial designs not exceeding 04 months and 20 days.
In complicated cases, the time limit for re-examination must be extended, however, it must not exceed the time limit for examination of applications for establishment of rights.
– Result: If the request is considered valid, the IPVN shall issue a decision on amendment of the protection title, register and publish it in the Industrial Property Official Gazette. If the request is considered invalid, the IPVN shall send to the requester a notice on its intended refusal. If within a set time limit the requester fails to correct errors or unsatisfactorily corrects errors, makes no opposition or an unreasonable opposition, the IPVN shall issue a decision on its rejection of the request for protection title amendment.
Return the protection title to the owner.
– Fees and charges:
+ Fee for examination request for amendment or change of holders of protection titles: VND 160,000/ 01 protection title;
+ Fee for publication of decision of amendment or change of holders of protection titles: VND 120,000/ 01 request;
– Fee for publication from the 2nd image onwards (if any): VND 60,000/ 01 image;
+ Fee for recording decision of amendment or change of holders of protection titles into the National Register of Industrial Property: VND 120,000/ protection title.
– Fee for a re-examination in case narrowing of the protection coverage: VND 700,000 / 01 variant.
4. General provisions on assignment of protection titles
Assignment of an industrial property right means the transfer of ownership right by owner of such industrial property right to another organization or individual. Assignment of industrial property rights must be established in the form of written contract (hereinafter referred to as “contract”).
An industrial property right assignment contract shall be valid upon its registration with the state management agency in charge of industrial property rights (IPVN).
– A dossier for registration of an industrial property right assignment contracts comprises the following documents:
+ Written declaration for registration of the contract on transfer of industrial property rights (made according to a set form 01-HĐCN Appendix D of Circular No. 01/2007/ TT-BKHCN);
+ The contract;
+ Original protection title;
+ Written consent of co-owners to the transfer of industrial property rights, if those industrial property rights are under common ownership;
+ Power of attorney (if the dossier is filed through a representative);
+ Fee and charge receipts;
+ Other documents (if necessary).
– The time limit: IPVN shall examine the requests for registration of assignment of protection titles within 02 months from the date of receipt of the request.
– Result: If a dossier for registration of an assignment of protection titles contains no error, the IPVN shall issue a decision on registration of the contract; register and publish it in the Industrial Property Official Gazette; If a dossier for registration of the contract contains errors, the IPVN shall send to the requester a notice on its intended refusal. If within a set time limit the requester fails to correct errors or unsatisfactorily corrects errors, makes no opposition or an unreasonable opposition, the IPVN shall issue a decision on its rejection of the request for protection title assignment.
Return (if any): the protection title to the owner.
– Fees and charges:
+ Fee for examination request for registration of assignment of protection titles: VND 230,000/ 01 protection title;
+ Fee for publication of decision of registration of assignment of protection titles: VND 120,000/ 01 request;
+ Fee for recording decision of registration of assignment of protection titles into the National Register of Industrial Property: VND 120,000/ 01 protection title.
5. General provisions on licensing of industrial property objects
Licensing of an industrial property object means the permission by the owner of such industrial property object for another organization or individual to use the industrial property object within the scope of his/her use right. Licensing of industrial property objects must be established in the form of written contracts (hereinafter referred to as “license contract”).
– A dossier for registration of a contract on licensing of an industrial property object (industrial property licensing contract) comprises the following documents:
+ Written declaration on the industrial property licensing contract (according to a set form 02-HĐSD Appendix D of Circular No. 01/2007/ TT-BKHCN);
+ 02 originals or 02 valid copies of the contract;
+ Written consent of co-owners to the licensing of the industrial property object, if the relevant industrial property rights are under common ownership;
+ Power of attorney (if the dossier is filed through a representative);
+ Fee and charge receipts;
+ Other documents (if necessary).
– The time limit: IPVN shall examine the requests for registration of the license contract within 02 months from the date of receipt of the request.
– Result: If a dossier for registration of an industrial property licensing contract contains no error, the IPVN shall issue a decision on the grant of a certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract; register and publish it in the Industrial Property Official Gazette; If a dossier for registration of the contract contains errors, the IPVN shall send to the requester a notice on its intended refusal. If within a set time limit the requester fails to correct errors or unsatisfactorily corrects errors, makes no opposition or an unreasonable opposition, the IPVN shall issue a decision on its rejection of the request for registration of an industrial property licensing contract.
Return (if any): certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract, the protection title to the owner.
– Fees and charges:
+ Fee for granting a certificate of registration of the contract of licensing of industrial property subject: VND 120,000/ 01 request;
+ Fee for examination request for registration of an industrial property licensing contract: VND 230,000/ 01 protection title;
+ Fee for publication of decision on the grant of a certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract: VND 120,000/ 01 request;
+ Fee for recording decision on the grant of a certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract into the National Register of Industrial Property: VND 120,000/ 01 protection title.
6. Recording of amendment of contents, extension and ahead-of-time termination of validity of contracts on licensing of industrial property objects
Amendment of the content of the industrial property licensing contract occurs in cases there is a change of name and address of the parties in the contract or changes in the content of the terms stated in the contract.
The extension of validity of the industrial property licensing contract occur in cases the parties agree to continue performing the contract after the term of the contract has expired, or the parties need to extend the validity of each IP object licensed in the contract.
Termination of the industrial property licensing contract occur in cases one of the parties requests to terminate the contract ahead of time.
The amendment of contents, extension and ahead-of-time termination of validity of registered contracts on licensing of industrial property objects shall all be recorded by the IPVN.
– A dossier requesting recording of amendment of contents, extension or ahead-of-time termination of validity of a contract on licensing of an industrial property object must be made in writing and comprise the following documents:
+ Written declaration requesting recording of amendment of contents, extension or termination of validity of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object (according to a set form 03-SĐHĐ Appendix D of Circular No. 01/2007/ TT-BKHCN);
+ The original certificate of registration of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object (in case of registration of amendment of contents or extension of validity of the contract);
+ Documents evidencing the amendment of the names and addresses of the contracting parties;
+ Agreements or documents on recording of specific contract clauses that need to be modified or supplemented, including the extension or ahead-of-time termination of validity of the contract;
+ Power of attorney (if the request is filed through a representative);
+ Fee and charge receipts;
+ Other documents (if necessary).
– The time limit: IPVN shall examine the requests for recording of amendment of contents, extension or ahead-of-time termination of validity of a contract on licensing of an industrial property object within 01 months from the date of receipt of the request.
– Result:
If the dossier is valid, the IPVN shall issue a decision on recording of amendment of contents, extension or termination of validity of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object; record the modified contents, extension of validity of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object in a certificate of registration of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object; record the modified contents, extension or termination of validity of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object in the national register of assignment of industrial property rights; publish the decision on recording of amendment of contents, extension or termination of validity of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object in the Industrial Property Official Gazette. If the dossier contains errors, the IPVN shall issue a notice on its intended refusal. If within a set time limit the requester fails to correct errors or unsatisfactorily corrects errors, makes no opposition or an unreasonable opposition, the IPVN shall issue a decision on its refusal to record the amendment of contents, extension or termination of validity of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object.
Return (if any): certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract that has updated the amendment or extension of the validity of the contract.
– Fees and charges:
+ Fee for examination request for recording of amendment of contents, extension or ahead-of-time termination of validity of an industrial property licensing contract: VND 160,000/ 01 protection title;
+ Fee for publication of decision on recording the modified contents, extension of validity of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object in a certificate of registration of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object: VND 120,000/ 01 request;
+ Fee for recording the modified contents, extension or termination of validity of the contract on licensing of an industrial property object into the National Register of Industrial Property: VND 120,000/ 01 protection title.
7. General provisions on grant of certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract duplicates and reissue of certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract
– A request for grant of duplicates/ reissue of certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contracts includes:
+ Declaration requesting grant of duplicates/ reissue of certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contracts (according to form 03-PBVB/GCN Appendix C of Circular No. 01/2007/ TT-BKHCN);
+ Power of attorney (in case the request is filed through a representative);
+ A copy of the receipt of fees and charges as prescribed;
+ Other documents (if necessary).
– The time limit: IPVN shall examine the request for grant of duplicates/ reissue of certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contracts within 01 month from the date of receipt of the request.
– Result: If that request satisfies the above requirements, the IPVN shall issue a decision on the grant of duplicate/ reissue of the certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract and publish it in the Industrial Property Gazette. If a request for duplicate/ reissue of a certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract fails to satisfy the requirements above, the IPVN shall issue a decision on its refusal to grant duplicates/ refusal to reissue the certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract.
Return the duplicated/ reissued certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract to the owner.
– Fees and charges:
+ Fee for publication of a decision on the grant of duplicate/ reissue of the certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract: VND 120,000/ 01 request;
+ Fee for recording a decision on the grant of duplicate/ reissue of the certificate of registration of an industrial property licensing contract into the National Register of Industrial Property: VND 120,000/ 01 protection title.
+ Public service fee (temporarily not calculated, will be collected when there are specific regulations).
8. Termination of validity of protection titles (its owner declares to relinquish the industrial property rights)
In this case, the termination of validity of protection titles due to the fact that its owner declares to relinquish the industrial property rights. Based on the result of the examination of requests for termination of validity of protection titles, the IPVN shall examine the request and decide to terminate the validity of such protection title from the date of receipt of the owner’s declaration.
– A request for termination of validity of protection title includes:
+ Declaration requesting termination of validity of protection titles (according to form 04-CDHB Appendix C of Circular No. 01/2007/ TT-BKHCN);
+ Written description of the reason for requesting the termination of validity of protection title;
+ Power of attorney (in case the request is filed through a representative);
+ A copy of the receipt of fees and charges as prescribed;
+ Other documents (if necessary).
– The time limit: IPVN shall examine the request for termination of validity of protection title within 10 days from the date of receipt of the request.
– Result: Based on the result of the examination of requests for termination of validity of protection titles and, the IPVN shall issue decisions on termination of validity of protection titles or notify the refusal to terminate the validity of protection titles.
– Fees and charges:
+ Fee for requests for termination of validity of protection titles: VND 50,000/ 01 request;
+ Fee for examination requests for termination of validity of protection titles: VND 180,000/ 01 protection title;
+ Fee for publication of decision on the termination of validity of protection titles: VND 120,000/ 01 request;
+ Fee for recording decision on the termination of validity of protection titles into the National Register of Industrial Property: VND 120,000/ 01 protection title.